When it comes to sports watches, most people recognize GPS (Global Positioning System) as the key satellite system enabling accurate location data, route tracking, and pacing information. However, most modern watches rely on multiple satellite systems, collectively known as Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), working together to deliver this precision. GPS is just one of the several systems these watches use, to provide the most accurate data possible to athletes and outdoor enthusiasts.
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) in Garmin Watches
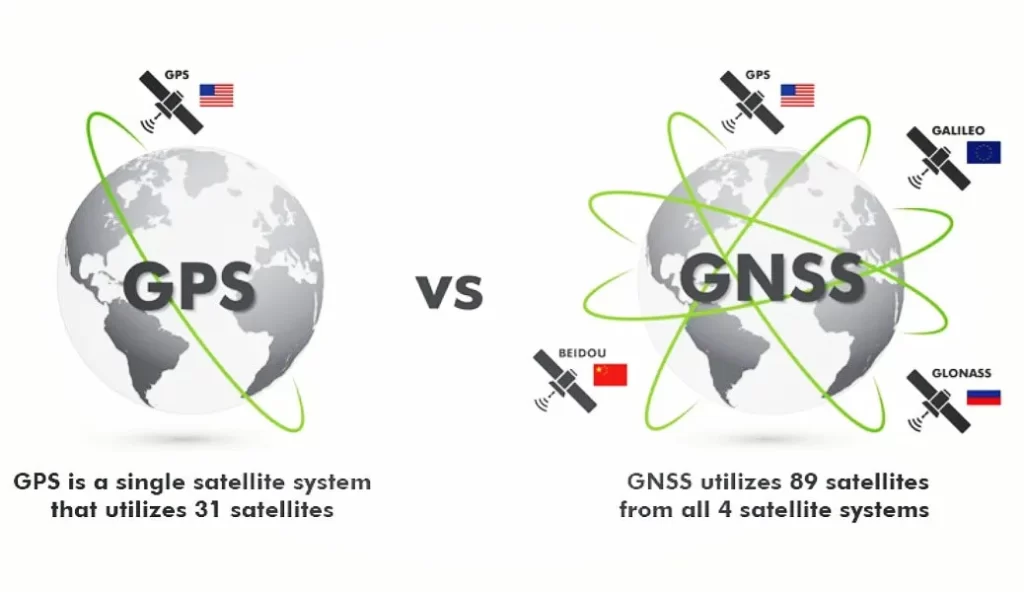
GNSS is a broad term that encompasses all satellite navigation systems used for determining positions on Earth. Most Garmin watches track multiple satellites within GNSS to enhance accuracy and reliability and it is referred to as “all systems”. These include GPS (United States), GLONASS (Russia), and Galileo (European Union), with some regional models also supporting BeiDou (China) and QZSS (Japan). By utilizing several satellite systems simultaneously, Garmin watches can deliver more precise location data than using one system alone.
Multi-Band GNSS: The Power of Dual-Frequency Technology
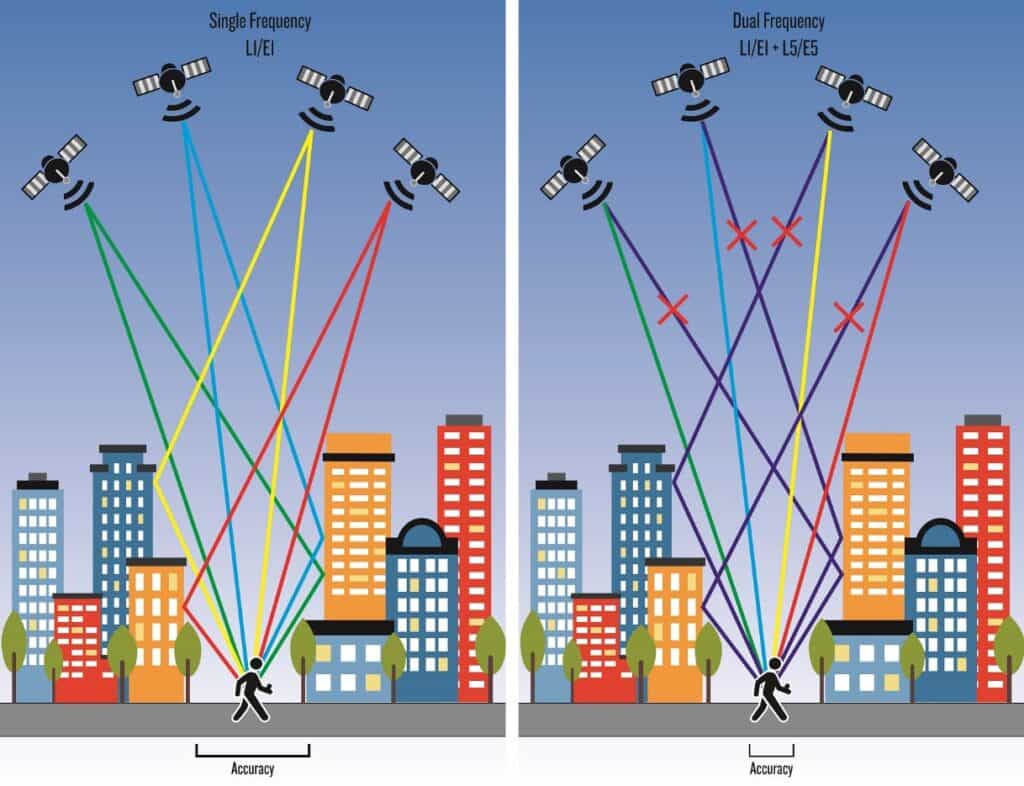
Another functionality to further improve location accuracy, now available on many of Garmin’s latest watch models is multi-band GNSS, also known as dual-frequency GNSS. Multi-band GNSS allows devices to receive signals on two different frequency bands from the same GNSS satellite system. It’s important to clarify that multi-band GNSS doesn’t mean connecting to multiple GNSS satellite systems, which has already been described above. Instead, it involves using different layers (frequencies) of signals from the satellites within those systems.

The key advantage of multi-band GNSS is that it can reduce errors caused by signal reflections and interference. By using signals on two different frequencies, multi-band GNSS can better distinguish and eliminate the effects of reflected signals, enhancing positioning accuracy by as much as 50% compared to single-band GNSS, particularly in urban settings with tall buildings or dense forests where obstructions are frequent.
Disadvantages of Multi-Band GNSS
While multi-band GNSS offers superior performance, there are trade-offs:
- Battery Life: Processing signals from multiple frequencies requires more power, which can reduce battery life by 20-40% compared to single-band GNSS.
- Device Cost: The technology and components required for multi-band GNSS might be more expensive, leading to more costly devices.
 Garmin Epix Pro Battery Life Comparison
Garmin Epix Pro Battery Life Comparison
SatIQ: Maximizing Battery Life with Smart Switching
Selecting multi-band GNSS (All + Multi-Band) on any Garmin device is one of many Satellite system options.

Many of the Garmin watches that include multi-band GNSS also offer a feature called SatIQ / AutoSelect. SatIQ intelligently switches between satellite modes based on the current environment. For instance, in open areas where a single frequency like GNSS is sufficient, SatIQ conserves battery life by sticking to that mode. However, when you enter environments with dense tree cover or tall buildings where higher accuracy is needed, SatIQ automatically activates multi-band GNSS. This smart switching not only ensures you get the accuracy when you need it but also helps extend battery life compared to keeping multi-band GNSS on continuously.

Multi-Band GNSS: Becoming the New Standard
Multi-band GNSS is quickly becoming the standard in the industry, with most new Garmin watches now including this functionality. This trend is not limited to Garmin; other companies like Coros and Apple have also embraced multi-band GNSS in their high-end devices.
The first Garmin watches to support multi-band GNSS were the Fenix 7 and Epix Gen 2 series, which launched in early 2022. At the time of this publication, other models launched with multi-band GNSS include: Enduro 2, Forerunner 255,955,265,965, Quatix 7, Tactix 7, Descent Mk3, Marq 2, Approach S70.
Is Multi-Band GNSS Worth It?
For users who demand the highest level of accuracy—whether for trail running, hiking in dense forests, or navigating city skyscrapers —multi-band GNSS offers clear advantages. With the addition of SatIQ, Garmin watches can intelligently manage battery consumption by only engaging multi-band GNSS when necessary, providing a balance between precision and battery life. As multi-band GNSS becomes the new standard across the industry, it’s likely to continue improving, providing even more accuracy while consuming less power.